Unveiling the Secrets of Peroxiredoxin Systems: A Comprehensive Guide in Subcellular Biochemistry 44

Peroxiredoxins are a family of multifunctional proteins that play critical roles in redox regulation, antioxidant defense, and signal transduction. They are found in all living organisms, from bacteria to humans, and their importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis is well-established.
4.6 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6517 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 422 pages |
In this comprehensive article, we delve into the fascinating world of peroxiredoxin systems, exploring their structures, functions, and subcellular roles. We draw from the latest research published in Subcellular Biochemistry 44, a renowned scientific journal dedicated to advancing our understanding of cellular processes.
Structure and Mechanism of Peroxiredoxins
Peroxiredoxins are small proteins typically composed of approximately 200 amino acids. They share a conserved catalytic domain that contains a cysteine residue essential for their antioxidant function.
The mechanism of action of peroxiredoxins involves a two-step process. In the first step, the cysteine residue in the catalytic domain reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2),forming a sulfenic acid intermediate. In the second step, the sulfenic acid intermediate undergoes a thiol-disulfide exchange reaction with a resolving cysteine residue, reducing the sulfenic acid back to a free thiol and generating a disulfide bond between the two cysteine residues.
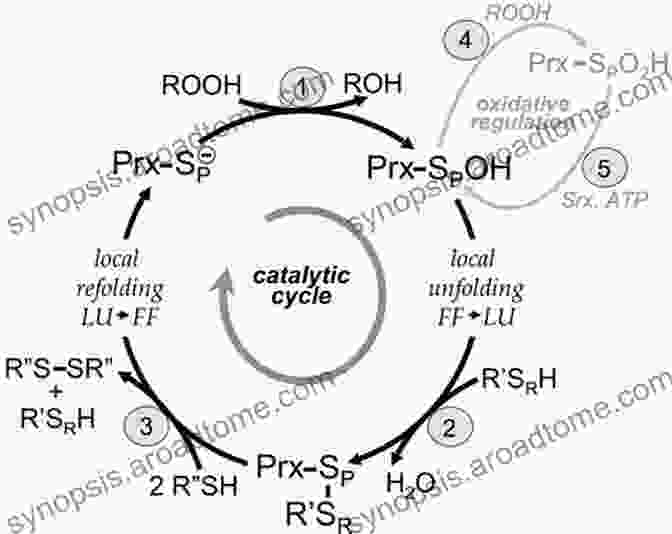
Functions of Peroxiredoxins
Peroxiredoxins perform a wide range of functions within cells, including:
- Antioxidant defense: Peroxiredoxins are crucial components of the cellular antioxidant defense system, protecting cells from oxidative stress caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as hydrogen peroxide.
- Redox regulation: Peroxiredoxins participate in redox signaling pathways, controlling the cellular redox environment and modulating the activity of redox-sensitive proteins.
- Signal transduction: Peroxiredoxins have been implicated in various signal transduction pathways, including those involved in cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Subcellular Localization of Peroxiredoxins
Peroxiredoxins are found in various subcellular compartments, including the cytosol, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and nucleus. Their subcellular localization determines their specific functions and interactions with other cellular components.
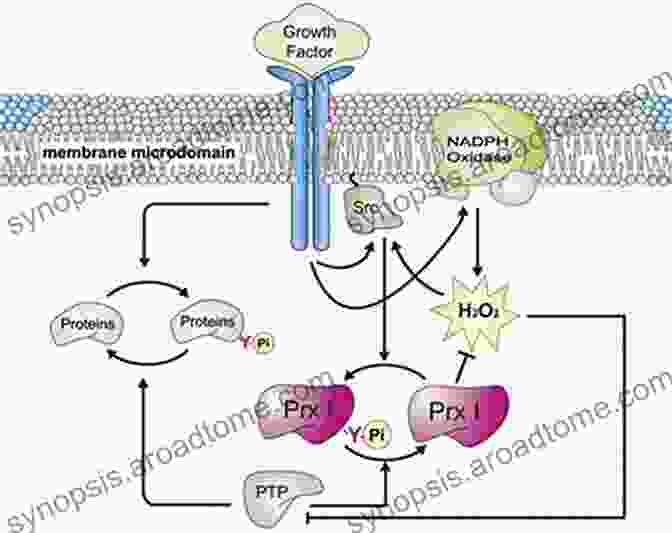
Physiological and Pathological Roles of Peroxiredoxins
Peroxiredoxins are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and protecting organisms from various diseases. They play crucial roles in:
- Immune response: Peroxiredoxins participate in immune cell function, regulating inflammation and the production of cytokines.
- Neurological function: Peroxiredoxins protect neurons from oxidative stress and contribute to normal brain development and function.
- Cardiovascular health: Peroxiredoxins are involved in the maintenance of vascular integrity and protect against cardiovascular diseases.
Dysregulation of peroxiredoxin systems has been linked to various pathological conditions, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular disFree Downloads.
Peroxiredoxins are fascinating and multifunctional proteins that play critical roles in cellular homeostasis and health. Their intricate structures, diverse functions, and subcellular localization contribute to their ability to protect cells from oxidative stress, regulate redox signaling, and participate in various physiological processes.
Subcellular Biochemistry 44 provides a comprehensive overview of peroxiredoxin systems, offering valuable insights into their mechanisms, functions, and pathological implications. This knowledge is essential for advancing our understanding of cellular biology and developing new therapeutic strategies for diseases associated with peroxiredoxin dysregulation.
4.6 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6517 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 422 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Gisele Sarmento
Gisele Sarmento David Glenn
David Glenn David E O Connor
David E O Connor Mia Fuller
Mia Fuller Mike Sacks
Mike Sacks Nicholas Tomihama
Nicholas Tomihama Sally John
Sally John David J H Smith
David J H Smith Dayna Winters
Dayna Winters David H Rosen
David H Rosen Garry Hamilton
Garry Hamilton Denise Linn
Denise Linn David Rivera
David Rivera Kristine Albrecht
Kristine Albrecht Meredith Schorr
Meredith Schorr David Phillips Hansen
David Phillips Hansen Deborah Mitchell
Deborah Mitchell June Mcdaniel
June Mcdaniel David R Foster
David R Foster Dawn J Sedgley
Dawn J Sedgley
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Tennessee WilliamsHogfather Novel of Discworld: A Literary Journey to the Realm of Terry...
Tennessee WilliamsHogfather Novel of Discworld: A Literary Journey to the Realm of Terry...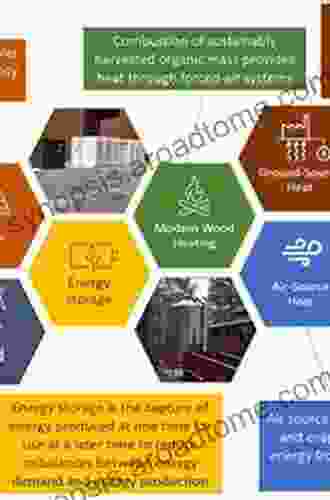
 Marcus BellUnlocking the Future of Energy: Dive into 'Introduction To Renewable Energy...
Marcus BellUnlocking the Future of Energy: Dive into 'Introduction To Renewable Energy...
 Isaac BellUnveiling the Enchanting World of Customs and Crafts: Recipes and Rituals for...
Isaac BellUnveiling the Enchanting World of Customs and Crafts: Recipes and Rituals for...
 William GoldingPiano Adventures Level Performance: The Ultimate Guide to Advanced Piano...
William GoldingPiano Adventures Level Performance: The Ultimate Guide to Advanced Piano... Allen GinsbergFollow ·7k
Allen GinsbergFollow ·7k Julian PowellFollow ·18.2k
Julian PowellFollow ·18.2k Giovanni MitchellFollow ·12k
Giovanni MitchellFollow ·12k Donovan CarterFollow ·15.7k
Donovan CarterFollow ·15.7k Elton HayesFollow ·7.5k
Elton HayesFollow ·7.5k Joe SimmonsFollow ·12.2k
Joe SimmonsFollow ·12.2k Al FosterFollow ·18.3k
Al FosterFollow ·18.3k Caleb LongFollow ·3.4k
Caleb LongFollow ·3.4k

 Isaac Bell
Isaac BellUnveiling the Enchanting World of Customs and Crafts:...
Embark on a captivating journey through the...

 Allen Parker
Allen ParkerHow to Write a Nonfiction Memoir: The Bookcraft Guide
Have you ever wanted...

 Nathaniel Powell
Nathaniel PowellCelebrate Spring's Arrival with Traditions from Around...
Immerse Yourself in the Vibrant Cultures of...
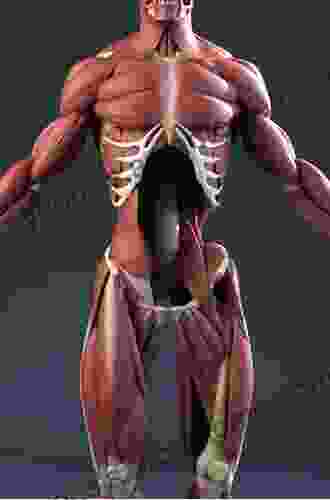
 Hunter Mitchell
Hunter MitchellThe Skeletal Muscles of the Human Body: An In-Depth Guide
The skeletal muscles of the human body are...

 Justin Bell
Justin BellFirst Aid for the NBDE: Your Essential Guide to Exam...
Master the NBDE...
4.6 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6517 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 422 pages |