Delve into the Mathematical Theory Behind Liquid Interfaces: A Comprehensive Guide

The world of liquid interfaces is a captivating realm where the laws of physics, chemistry, and mathematics intertwine to create a symphony of complex phenomena. From the iridescent shimmer of soap bubbles to the intricate dynamics of capillary waves, liquid interfaces exhibit a mesmerizing array of behaviors that have fascinated scientists and mathematicians for centuries.
At the heart of this scientific exploration lies the mathematical theory of liquid interfaces, a discipline that provides a rigorous framework for understanding the behavior of these enigmatic systems. This article will delve into the depths of this theory, shedding light on its fundamental concepts, powerful tools, and far-reaching applications.
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 9622 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 224 pages |
The Essence of Liquid Interfaces
A liquid interface is the boundary between two fluids, such as a liquid and a gas or two immiscible liquids. These interfaces are characterized by unique properties that stem from the interplay of surface tension, intermolecular forces, and hydrodynamic effects.
Surface tension, the energy required to increase the area of an interface, is a key player in shaping the behavior of liquid interfaces. It drives the formation of spherical droplets, minimizes the surface area of liquid bodies, and gives rise to capillary forces.
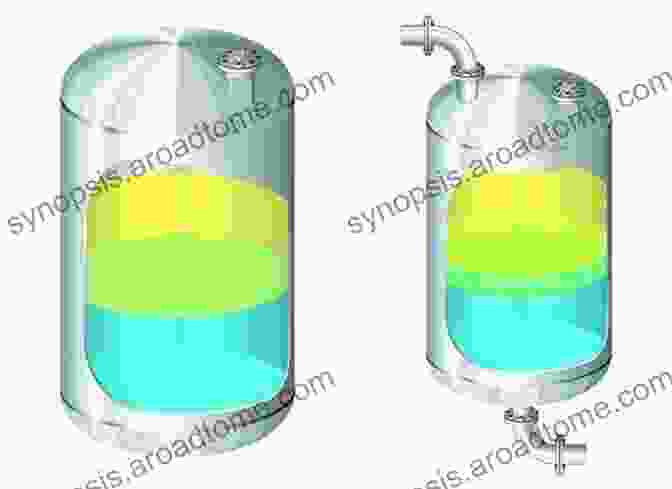

Intermolecular forces, such as van der Waals forces and electrostatic interactions, also play a crucial role in determining the properties of liquid interfaces. These forces can lead to the formation of Free Downloaded structures, such as Langmuir monolayers and liquid crystals, at the interface.
Hydrodynamic effects, arising from the motion of fluids, can significantly influence the behavior of liquid interfaces. These effects include viscous dissipation, which can damp out capillary waves, and hydrodynamic instabilities, which can lead to the breakup of liquid droplets.
The Mathematical Toolkit
The mathematical theory of liquid interfaces employs a diverse set of mathematical tools to unravel the complexities of these systems. These tools include:
- Continuum mechanics: This branch of mathematics provides a framework for describing the macroscopic behavior of fluids, including their velocity, pressure, and density.
- Fluid dynamics: This field deals with the motion of fluids and the forces acting upon them. Fluid dynamics is essential for understanding the hydrodynamic effects that influence liquid interfaces.
- Thermodynamics: This discipline provides a framework for understanding the energy and entropy changes associated with liquid interfaces. Thermodynamics is crucial for studying phenomena such as wetting and spreading.
- Statistical mechanics: This field provides a statistical framework for understanding the behavior of large collections of molecules. Statistical mechanics is used to study the formation of Free Downloaded structures at liquid interfaces.
- Numerical methods: These techniques are used to solve complex mathematical models that describe liquid interfaces. Numerical methods are essential for simulating and analyzing the behavior of these systems.
Key Concepts in the Mathematical Theory
The mathematical theory of liquid interfaces revolves around several key concepts that provide a deeper understanding of these systems:
- Surface tension: Surface tension is a fundamental property of liquid interfaces that arises from the unbalanced intermolecular forces at the interface. It is responsible for the formation of spherical droplets, the minimization of surface area, and capillary forces.
- Capillary length: The capillary length is a characteristic length scale that determines the relative importance of surface tension and gravity in liquid interfaces. It is used to characterize phenomena such as capillary waves and capillary rise.
- Contact angle: The contact angle is the angle between a liquid interface and a solid surface. It is determined by the balance of surface tension, intermolecular forces, and wetting properties.
- Wetting and spreading: Wetting refers to the ability of a liquid to spread on a solid surface. Spreading is driven by the minimization of surface energy and is influenced by the contact angle.
- Capillary waves: Capillary waves are small-amplitude waves that propagate along liquid interfaces. They are driven by surface tension and are characterized by their wavelength and frequency.
Applications of the Mathematical Theory
The mathematical theory of liquid interfaces has far-reaching applications in a wide range of scientific and engineering disciplines, including:
- Chemical engineering: The theory is used to design and optimize processes that involve liquid interfaces, such as separation, mixing, and coating.
- Materials science: The theory is used to study the behavior of liquid interfaces in materials, such as polymers, colloids, and emulsions.
- Biophysics: The theory is used to understand the behavior of liquid interfaces in biological systems, such as cell membranes and protein-lipid interactions.
- Microfluidics: The theory is used to design and optimize microfluidic devices that manipulate liquid interfaces for applications in diagnostics, drug delivery, and microfabrication.
- Environmental science: The theory is used to study the behavior of liquid interfaces in environmental systems, such as the formation of oil spills, the transport of pollutants, and the remediation of contaminated soil.
The mathematical theory of liquid interfaces is a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of these complex systems. By harnessing the power of mathematics, scientists and engineers can gain insights into the fundamental properties of liquid interfaces and develop innovative applications that harness their unique capabilities.
As research in this field continues to advance, we can expect even more exciting discoveries and applications of the mathematical theory of liquid interfaces in the years to come.
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 9622 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 224 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia David Kempston
David Kempston David Hirsh
David Hirsh Eric H Cline
Eric H Cline Delia Parr
Delia Parr Jim Lewis
Jim Lewis Daymond John
Daymond John Kathrin A Stauffer
Kathrin A Stauffer Junior Tay
Junior Tay David Ohrvall
David Ohrvall David Tzemach
David Tzemach David Fletcher
David Fletcher Jon Kelly
Jon Kelly David G Mcafee
David G Mcafee David Diamantes
David Diamantes Tom Marioni
Tom Marioni Garry Hunter
Garry Hunter Michael Mcgrath
Michael Mcgrath Debbie Indyk
Debbie Indyk Lynn Melchiori
Lynn Melchiori Susan Warner
Susan Warner
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Paulo CoelhoUnlock Your Musical Potential: Turn Your Spare Room Into a Hit Factory with...
Paulo CoelhoUnlock Your Musical Potential: Turn Your Spare Room Into a Hit Factory with...
 Junichiro TanizakiThe Of Many Flames: A Literary Masterpiece that Illuminates the Darkness
Junichiro TanizakiThe Of Many Flames: A Literary Masterpiece that Illuminates the Darkness Howard BlairFollow ·9.2k
Howard BlairFollow ·9.2k Haruki MurakamiFollow ·18.3k
Haruki MurakamiFollow ·18.3k Alex FosterFollow ·11.4k
Alex FosterFollow ·11.4k Felix HayesFollow ·5.7k
Felix HayesFollow ·5.7k Chase MorrisFollow ·2.4k
Chase MorrisFollow ·2.4k Kyle PowellFollow ·7.8k
Kyle PowellFollow ·7.8k Corey HayesFollow ·16.1k
Corey HayesFollow ·16.1k Hunter MitchellFollow ·7.9k
Hunter MitchellFollow ·7.9k

 Isaac Bell
Isaac BellUnveiling the Enchanting World of Customs and Crafts:...
Embark on a captivating journey through the...

 Allen Parker
Allen ParkerHow to Write a Nonfiction Memoir: The Bookcraft Guide
Have you ever wanted...

 Nathaniel Powell
Nathaniel PowellCelebrate Spring's Arrival with Traditions from Around...
Immerse Yourself in the Vibrant Cultures of...
 Hunter Mitchell
Hunter MitchellThe Skeletal Muscles of the Human Body: An In-Depth Guide
The skeletal muscles of the human body are...

 Justin Bell
Justin BellFirst Aid for the NBDE: Your Essential Guide to Exam...
Master the NBDE...
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 9622 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 224 pages |