Atrial Frustration: A Cardiac Arrhythmia Saga

The human heart, an intricate marvel of nature, orchestrates a symphony of electrical impulses that govern its rhythmic contractions. However, at times, this delicate balance can be disrupted, leading to cardiac arrhythmias, deviations from the normal heart rhythm. Among these arrhythmias, atrial frustration stands out as a prevalent enigma, captivating the attention of cardiologists and electrophysiologists alike.
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 10459 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 252 pages |
Unveiling Atrial Frustration: The Enigma
Atrial frustration, an elusive entity in the realm of cardiac arrhythmias, arises from a paradoxical interplay between the heart's atria (upper chambers) and ventricles (lower chambers). Normally, electrical impulses originating in the sinoatrial node, the heart's natural pacemaker, seamlessly navigate through the atria, causing them to contract in a coordinated fashion. However, in atrial frustration, an obstacle arises, impeding the electrical signals' journey from the atria to the ventricles.
This obstruction, often attributed to prolonged atrial activation time or impaired conduction through the atrioventricular node, triggers a cascade of events that culminate in atrial frustration. Instead of effectively initiating ventricular contractions, the electrical impulses become trapped within the atria, causing them to quiver fruitlessly. This futile atrial activity, devoid of ventricular response, characterizes atrial frustration.
Exploring the Clinical Spectrum
Atrial frustration manifests in a diverse range of clinical presentations, mirroring the multifaceted nature of its underlying mechanisms. Patients may experience palpitations, a fluttering sensation in their chests, or a rapid and irregular heartbeat. Some individuals remain asymptomatic, unaware of the arrhythmia's presence until it is detected during a routine checkup or prompted by an unrelated medical issue.
In severe cases, atrial frustration can culminate in debilitating symptoms. Persistent atrial arrhythmias can weaken the heart muscle, leading to heart failure. Additionally, atrial frustration increases the risk of thromboembolic events, such as strokes, due to the formation of blood clots within the quivering atria.
Diagnostic Odyssey: Unmasking Atrial Frustration
Unraveling the enigma of atrial frustration demands a meticulous diagnostic approach. Electrocardiography (ECG),a cornerstone of cardiac assessment, provides valuable insights into the heart's electrical activity. ECG tracings in atrial frustration typically reveal the absence of P waves, representing atrial depolarization, followed by irregular ventricular complexes.
However, ECG findings alone may not suffice to definitively diagnose atrial frustration. Advanced diagnostic techniques, such as Holter monitoring and electrophysiological studies, play a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis and differentiating atrial frustration from other arrhythmias. Holter monitoring involves wearing a portable ECG device for 24 hours or more, capturing a comprehensive record of the heart's electrical activity during daily activities. Electrophysiological studies, more invasive procedures, meticulously map the electrical pathways of the heart, pinpointing the source of the arrhythmia and guiding treatment decisions.
Therapeutic Strategies: Navigating the Treatment Maze
Tackling atrial frustration often entails a multifaceted approach, tailored to the individual patient's needs and the underlying cause of the arrhythmia. Medications, including antiarrhythmics and beta-blockers, aim to control the heart rate and restore a regular rhythm. For more persistent or severe cases, catheter ablation, a minimally invasive procedure, offers a promising solution. This technique involves threading a catheter through the blood vessels to the heart, where energy is delivered to ablate (destroy) the arrhythmogenic tissue, effectively eliminating the source of the atrial frustration.
In select cases, implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) or pacemakers may be necessary to prevent sudden cardiac death or maintain a regular heart rhythm. ICDs constantly monitor the heart's rhythm, delivering shocks to terminate life-threatening arrhythmias. Pacemakers, on the other hand, provide electrical impulses to the heart when its natural pacemaker fails or becomes irregular, ensuring a consistent and adequate heart rate.
Prognostic Nuances: Unveiling the Crystal Ball
The prognosis for atrial frustration varies depending on the underlying cause, severity of the arrhythmia, and the patient's overall health. While some individuals experience only mild symptoms and require minimal treatment, others face a more challenging journey, necessitating aggressive interventions and close monitoring.
Atrial fibrillation, a common type of atrial frustration, poses a significant risk of stroke. However, early detection and proper management can mitigate this risk and improve the overall prognosis. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC),a rare but potentially fatal condition, can manifest as atrial frustration and requires specialized care to prevent sudden cardiac death.
: Embracing the Heart's Rhythm
Atrial frustration, a multifaceted cardiac arrhythmia, presents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. However, with advancements in electrophysiology and tailored treatment approaches, the prognosis for individuals with atrial frustration continues to improve. By unraveling the intricacies of this enigmatic arrhythmia, we empower ourselves to alleviate its burden and restore the heart's harmonious rhythm.
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 10459 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 252 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Deirdre Imus
Deirdre Imus Derald Wing Sue
Derald Wing Sue Deniz Aydoslu
Deniz Aydoslu David Radoff
David Radoff Sharada Sugirtharajah
Sharada Sugirtharajah David Tracey
David Tracey David Parker
David Parker Deborah Lock
Deborah Lock Joseph E Muscolino
Joseph E Muscolino Deborah Durbin
Deborah Durbin Graham Haley
Graham Haley Debbie Sardone
Debbie Sardone Jessica Bellinger
Jessica Bellinger Derek J Barnard
Derek J Barnard Joey Barnett
Joey Barnett Diana Jacobs
Diana Jacobs Deann Blakeman
Deann Blakeman Stewart A Dippel
Stewart A Dippel Debbie Hardy
Debbie Hardy Denis Mukwege
Denis Mukwege
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Corbin PowellThe Apostate: My Search for Truth - Embark on an Unforgettable Journey of...
Corbin PowellThe Apostate: My Search for Truth - Embark on an Unforgettable Journey of... Hunter MitchellFollow ·7.9k
Hunter MitchellFollow ·7.9k Kelly BlairFollow ·13.9k
Kelly BlairFollow ·13.9k Gabriel BlairFollow ·4.4k
Gabriel BlairFollow ·4.4k DeShawn PowellFollow ·13.3k
DeShawn PowellFollow ·13.3k Joseph HellerFollow ·19.5k
Joseph HellerFollow ·19.5k Colt SimmonsFollow ·4.5k
Colt SimmonsFollow ·4.5k Winston HayesFollow ·14.9k
Winston HayesFollow ·14.9k Edwin BlairFollow ·18.8k
Edwin BlairFollow ·18.8k

 Isaac Bell
Isaac BellUnveiling the Enchanting World of Customs and Crafts:...
Embark on a captivating journey through the...

 Allen Parker
Allen ParkerHow to Write a Nonfiction Memoir: The Bookcraft Guide
Have you ever wanted...

 Nathaniel Powell
Nathaniel PowellCelebrate Spring's Arrival with Traditions from Around...
Immerse Yourself in the Vibrant Cultures of...
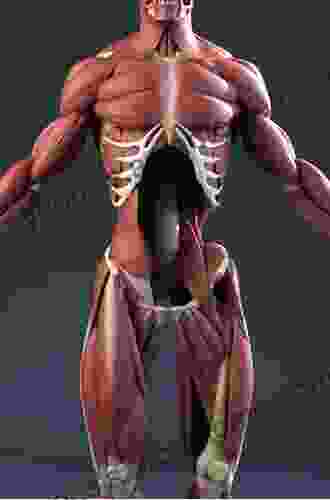
 Hunter Mitchell
Hunter MitchellThe Skeletal Muscles of the Human Body: An In-Depth Guide
The skeletal muscles of the human body are...

 Justin Bell
Justin BellFirst Aid for the NBDE: Your Essential Guide to Exam...
Master the NBDE...
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 10459 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 252 pages |